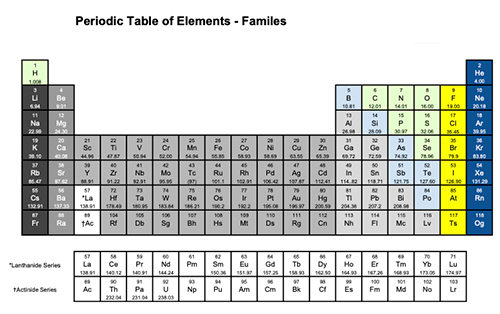
What is Polymerization?
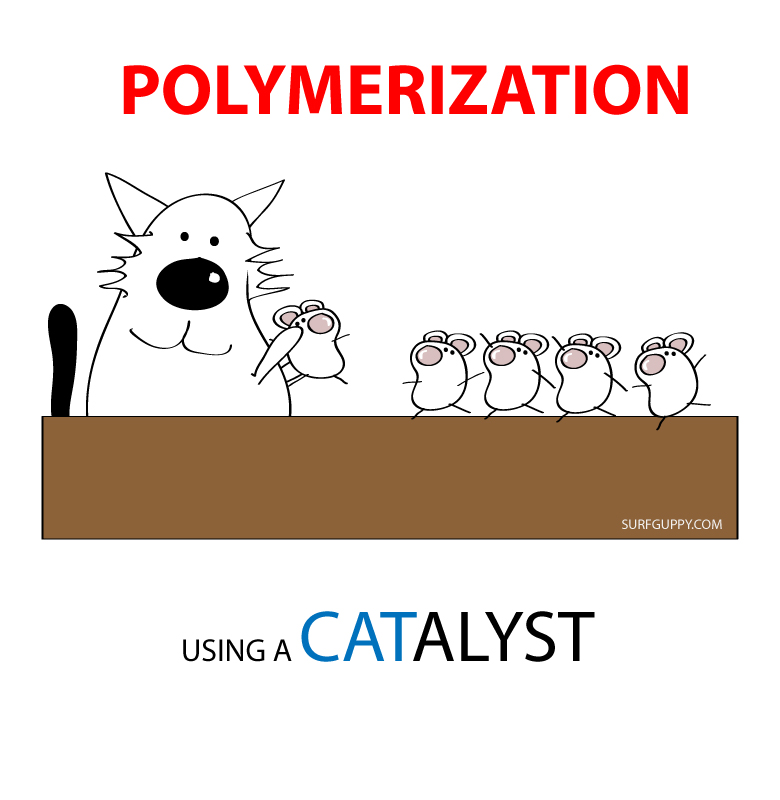
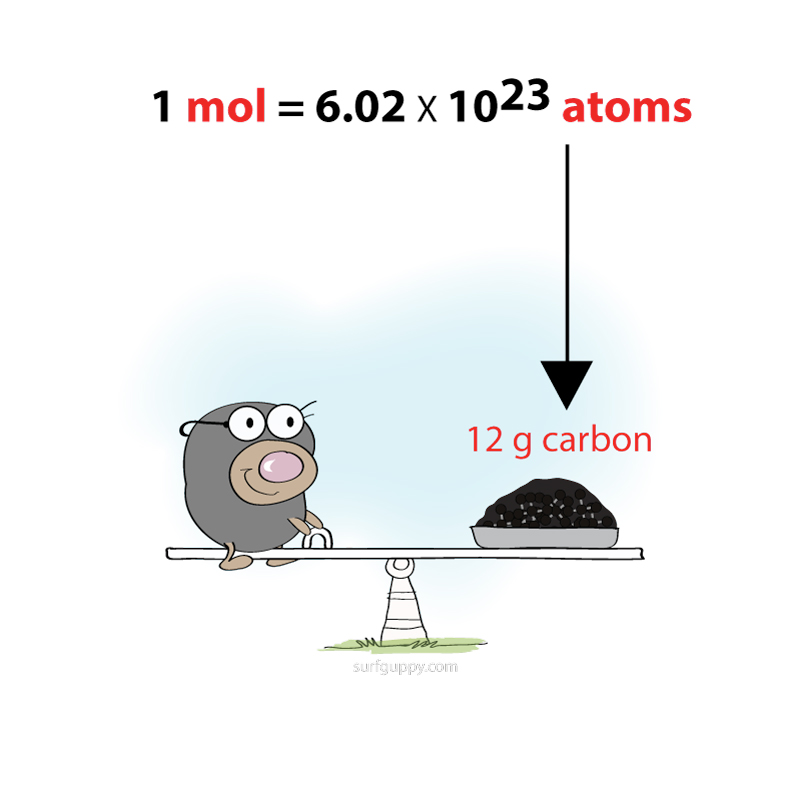
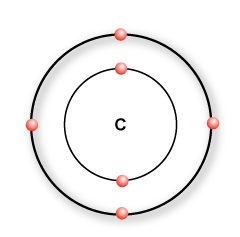
Polymerization is simply the process of putting together monomers (single molecules), to become a long chain of molecules (called polymers) with the use of a catalyst.
Polymerization is an important process for making plastics.
A catalyst

A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change.… Read the rest









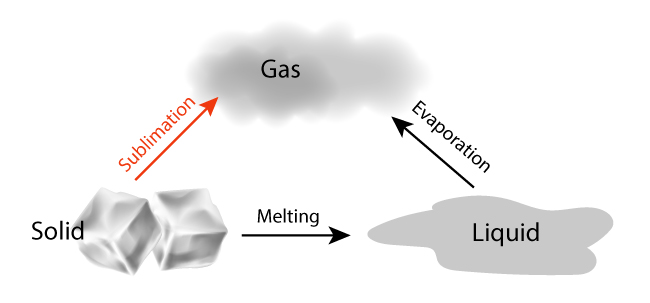
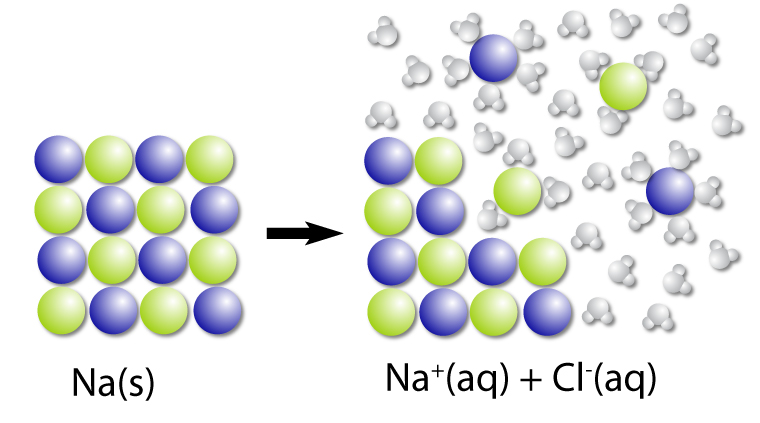

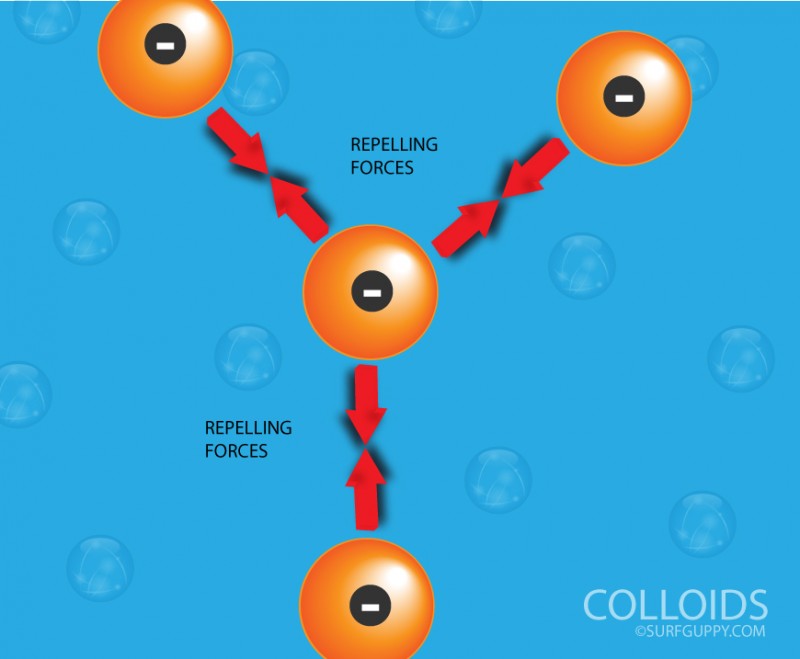



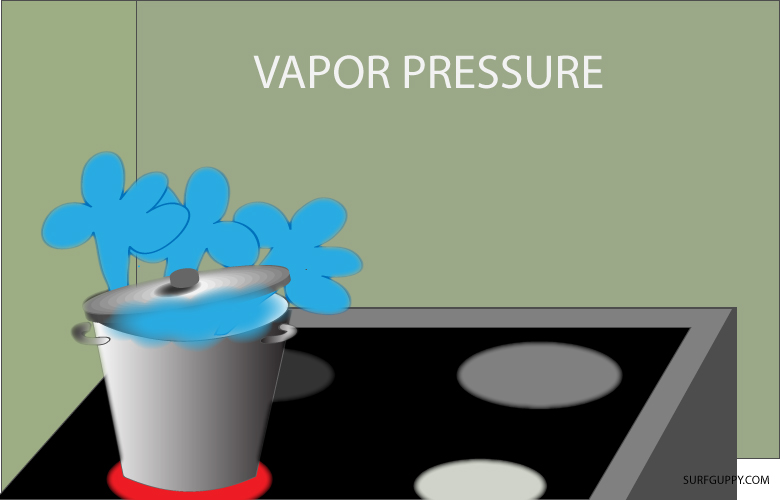
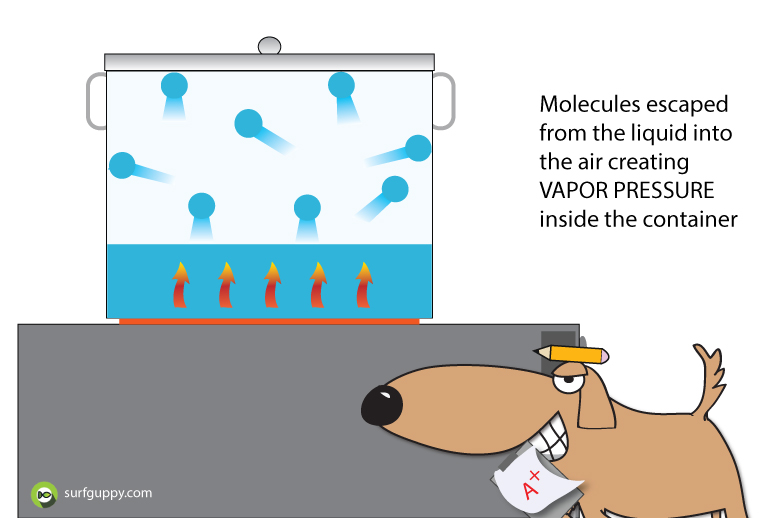
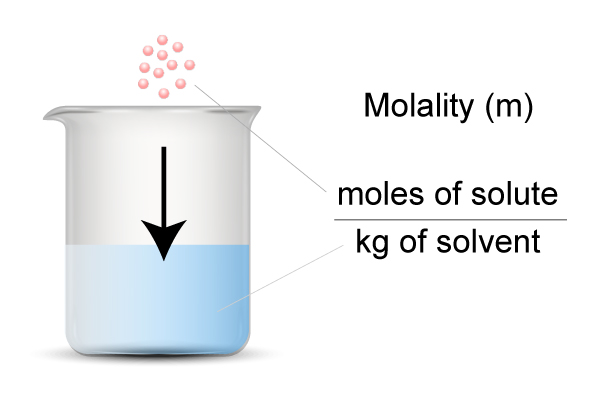
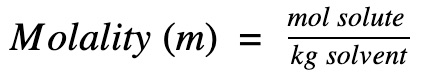


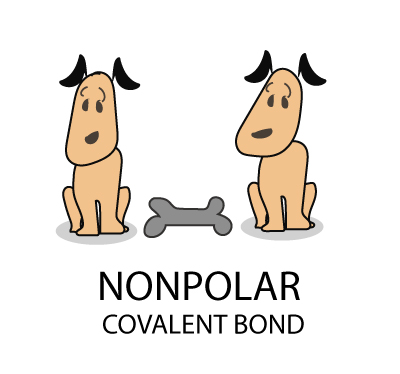
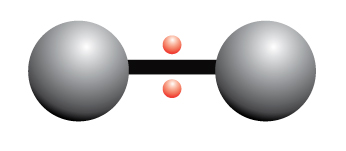
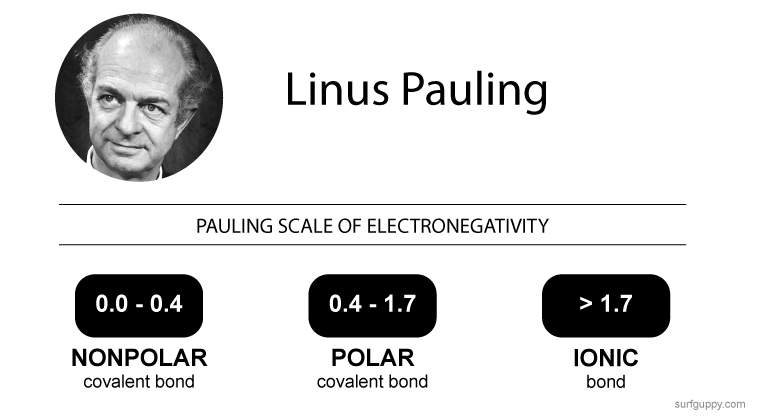
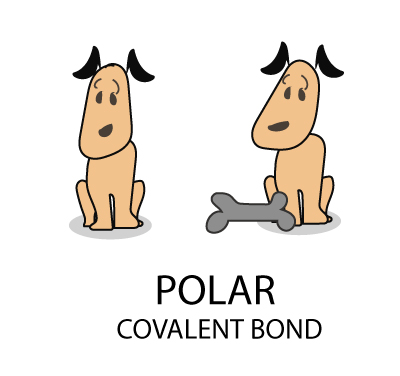
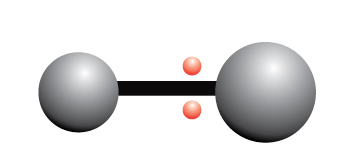
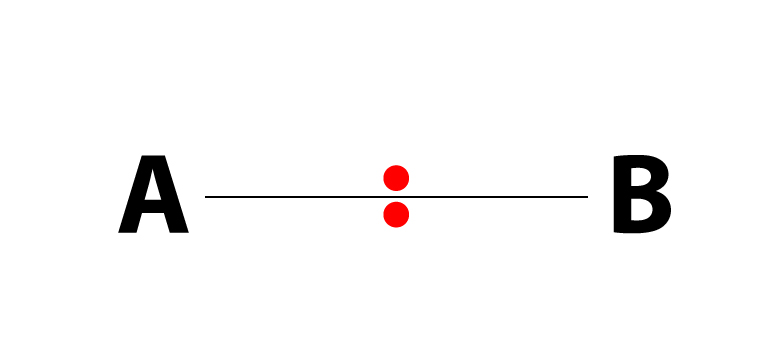
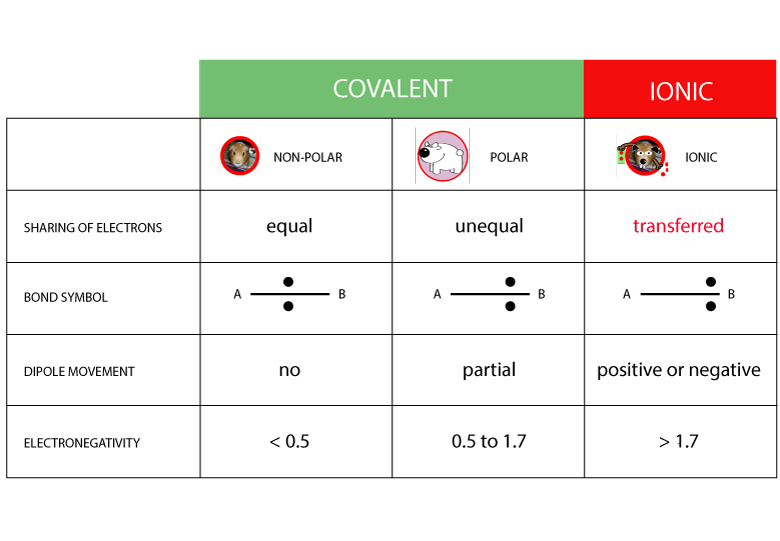



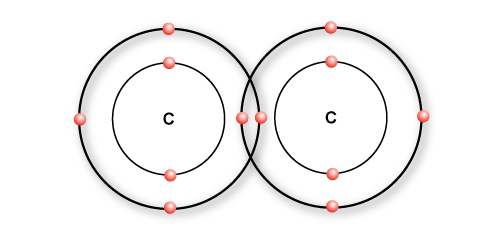
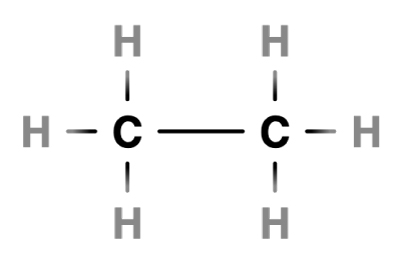



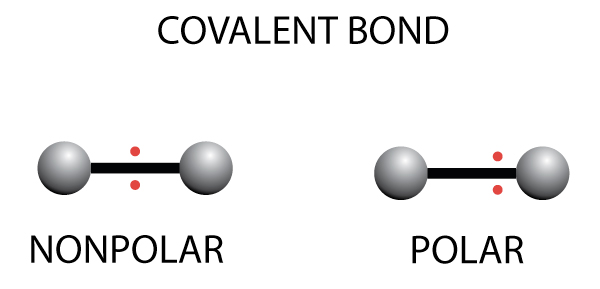 …
… 



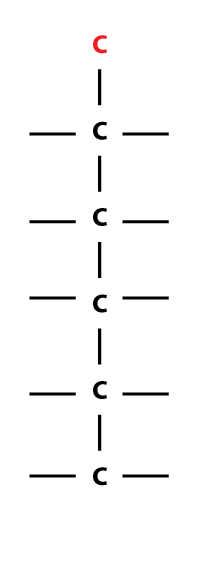
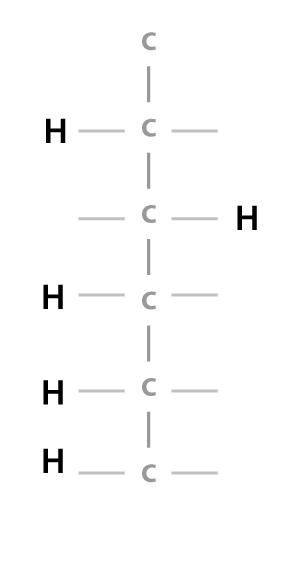

 …
… 








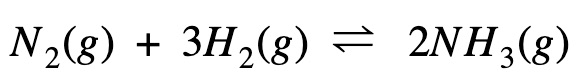

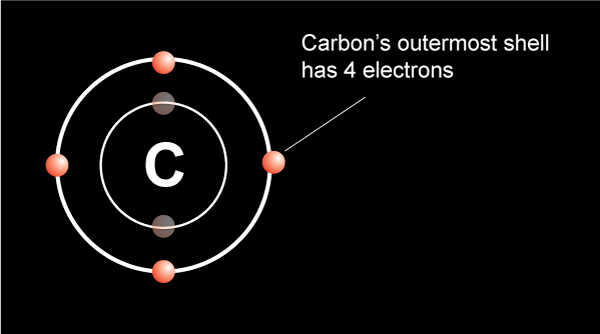

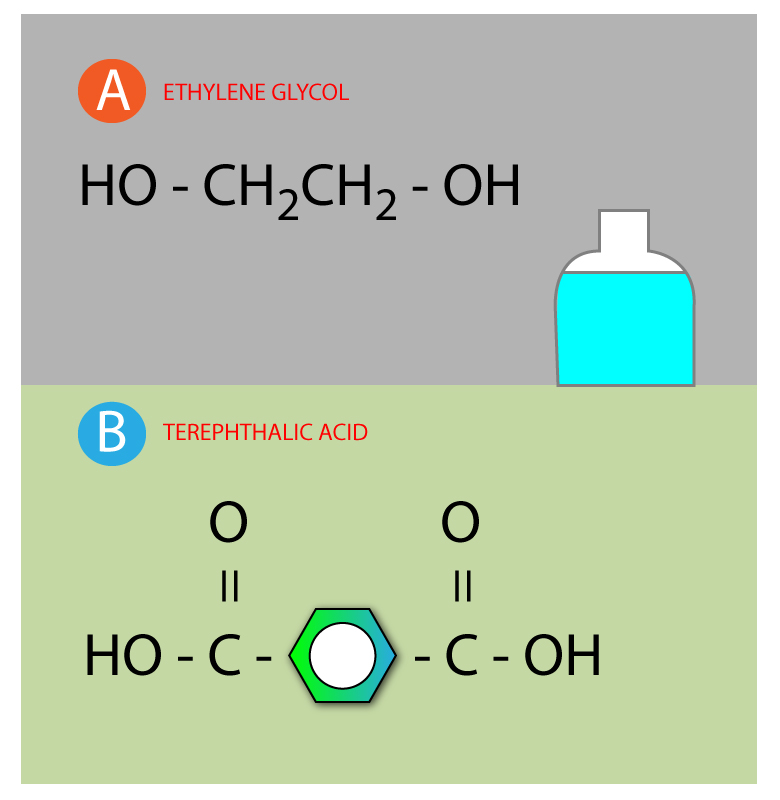
 This pretty symbol you see is called an ester linkage formed by combining acid and an alcohol.…
This pretty symbol you see is called an ester linkage formed by combining acid and an alcohol.… 
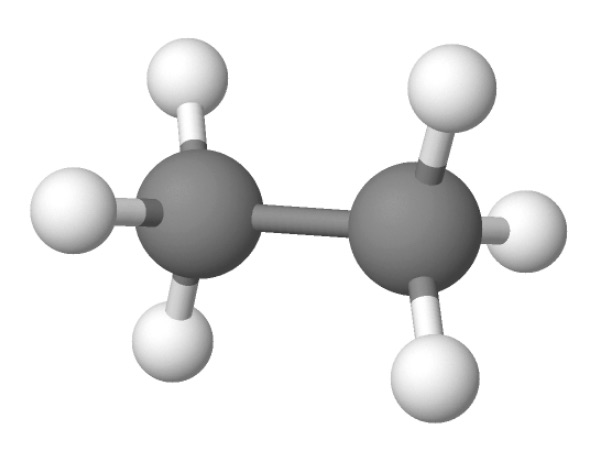
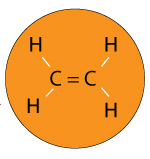 Imagine you have a polymer called Ethylene.
Imagine you have a polymer called Ethylene.