Sublimation
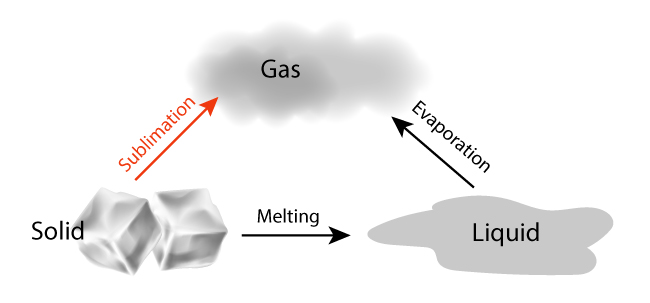
WHAT TYPE OF SOLID SUBLIMES? We all know that ice melts before it evaporates. In sublimation, the liquid phased is omitted.

WHAT TYPE OF SOLID SUBLIMES? We all know that ice melts before it evaporates. In sublimation, the liquid phased is omitted.
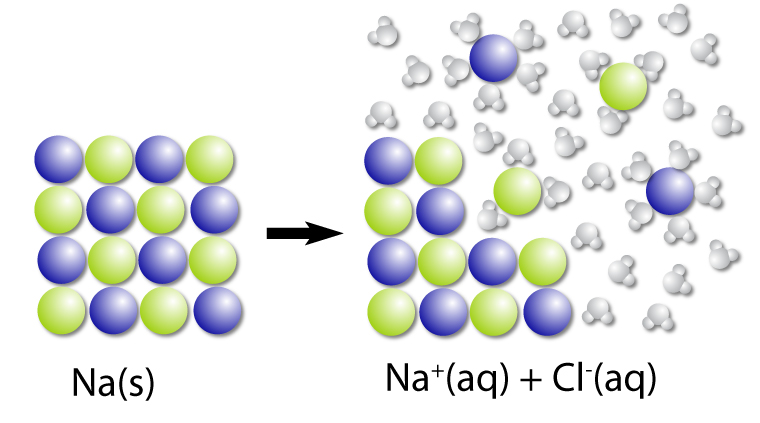
Dissociation is the breaking down of a compound into elements and the process is usually reversible.

In 1784, a French physicist and clergyman named Jean Antoine Nollet made an interesting discovery. He filled a pig’s bladder with a concentrated solution of alcohol. He then put the bladder in water and the bladder expanded! This interesting process Read More …
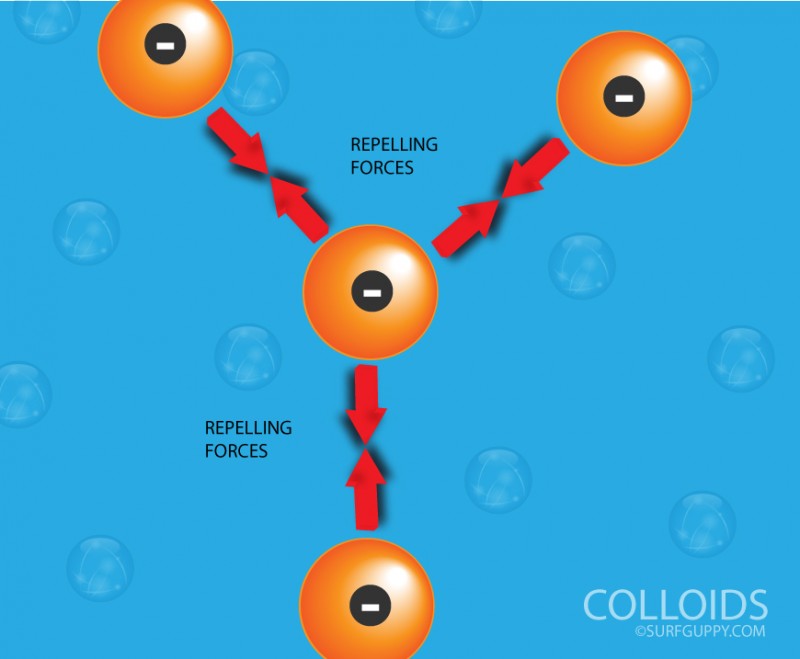
Do you know that the cloudy water syndrome in a fish tank is caused by colloids? Over a period of time, organic waste produced by the fish and algae in the tank are turned into nitrates. These particles are interspersed Read More …

Irregular motion of suspended particles is called “Brownian motion”. Watch an interesting Youtube video on the discovery of Brownian Motion by British botanist Robert Brown Robert Brown was a Scottish botanist who first discovered the Brownian motion. He noticed random Read More …
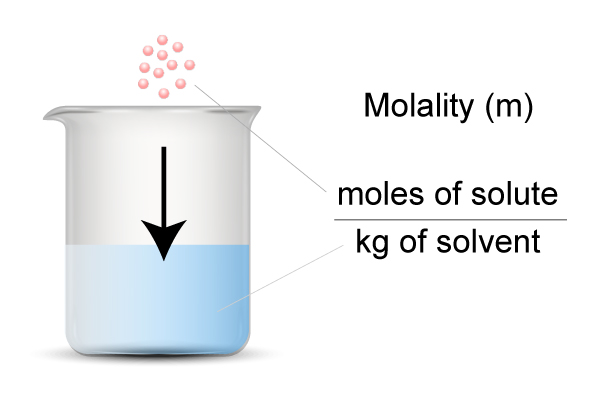
Molality is defined as the number of moles of solute per 1 (kg) of solvent. Solute = particles you dissolve Solvent = the liquid you use for dissolving the particles Example Calculate molality (m) of 29.8 g of glucose (C6H12O6) dissolved in Read More …

Nonpolar molecules do not dissolve readily in water Nonpolar molecules do not become hydrated – they are repelled by water The molecules are insoluble or almost insoluble in water Oils and fats are examples of hydrophobic substances. For example, if you mix Read More …

The solubility of a substance is the amount of that substance that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent. The difference between solute and solvent SOLUTE – the substance to be dissolved SOLVENT – the liquid for dissolving the Read More …