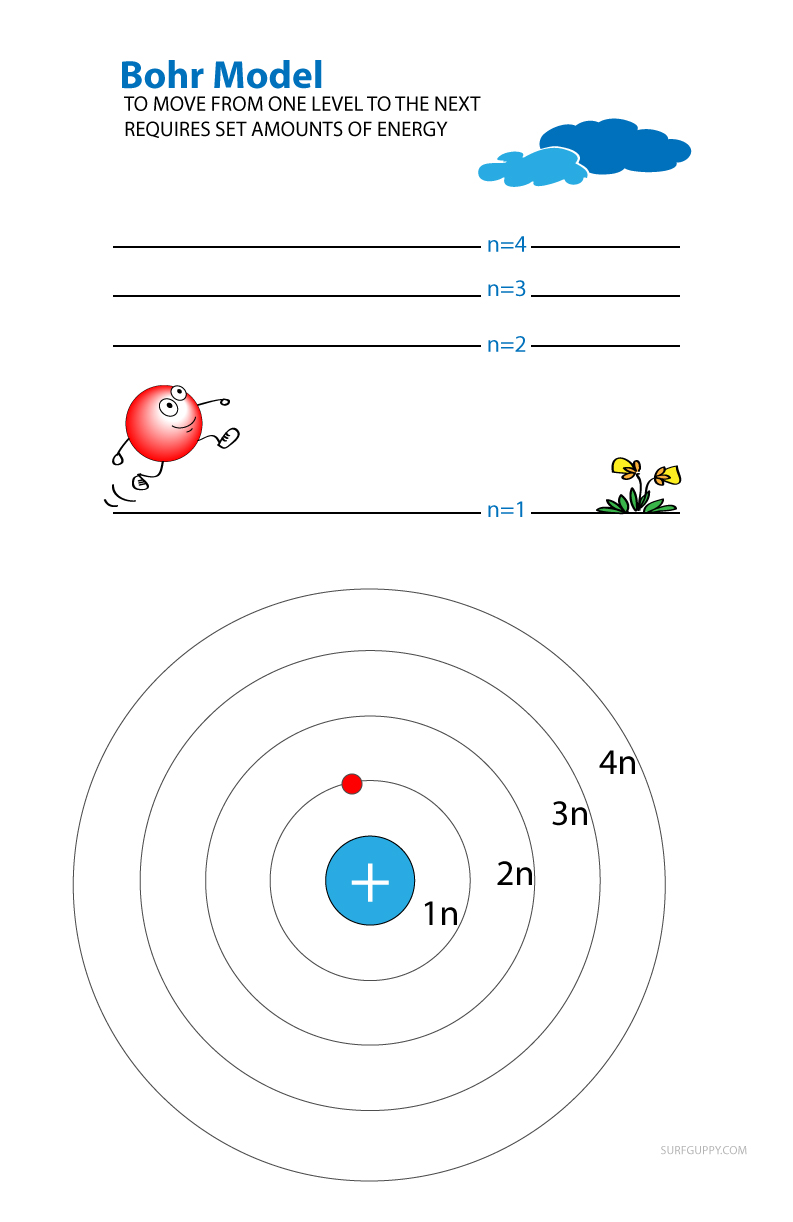
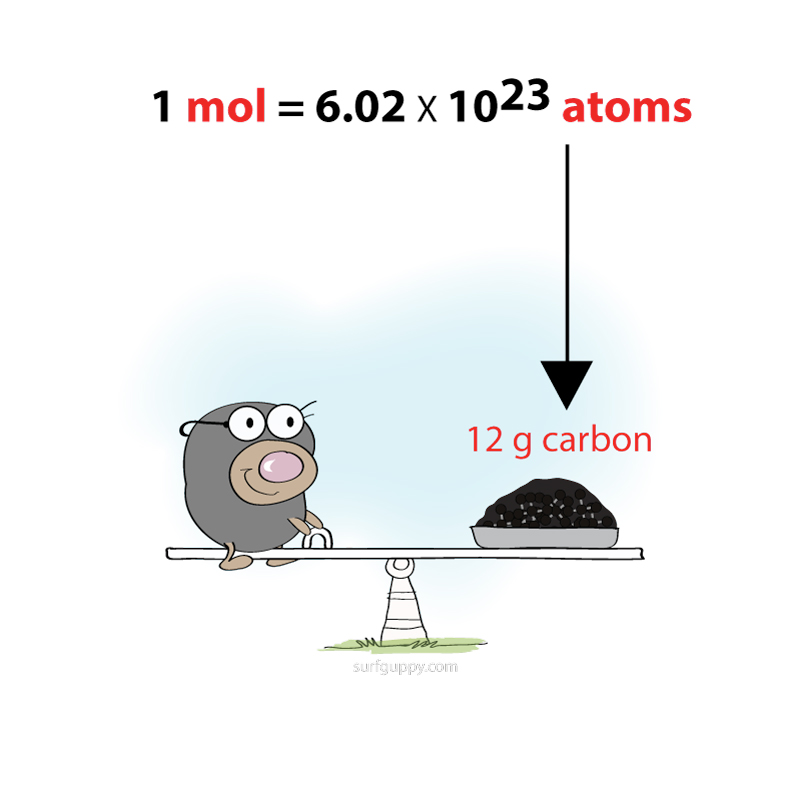
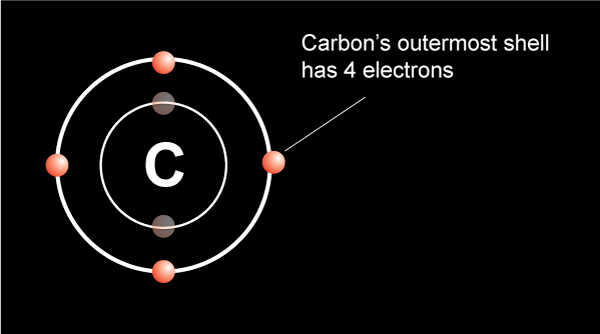
Why is water polar?
Why is water polar and why is the water molecule a bent shape?
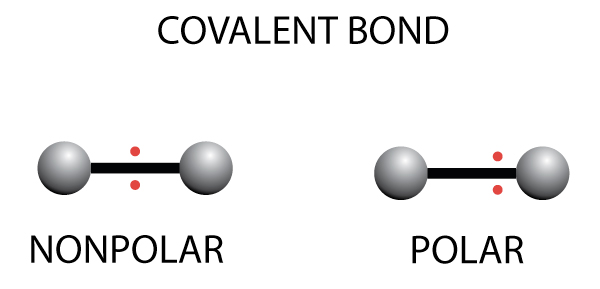
Water is polar because it has one end that is slightly negatively charged, and another end that is positively charged.
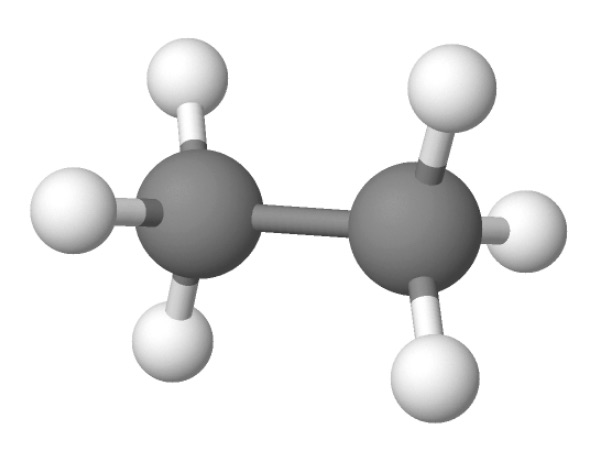
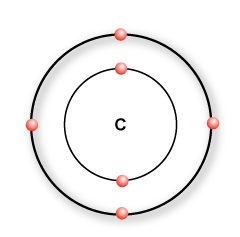
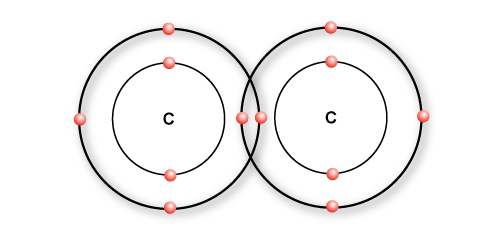
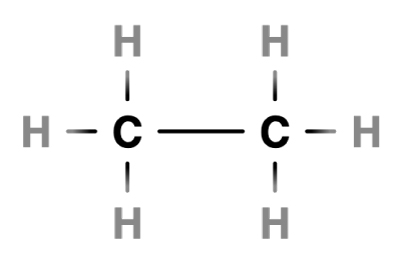
The water molecule is made of one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms.… Read the rest





 …
… 
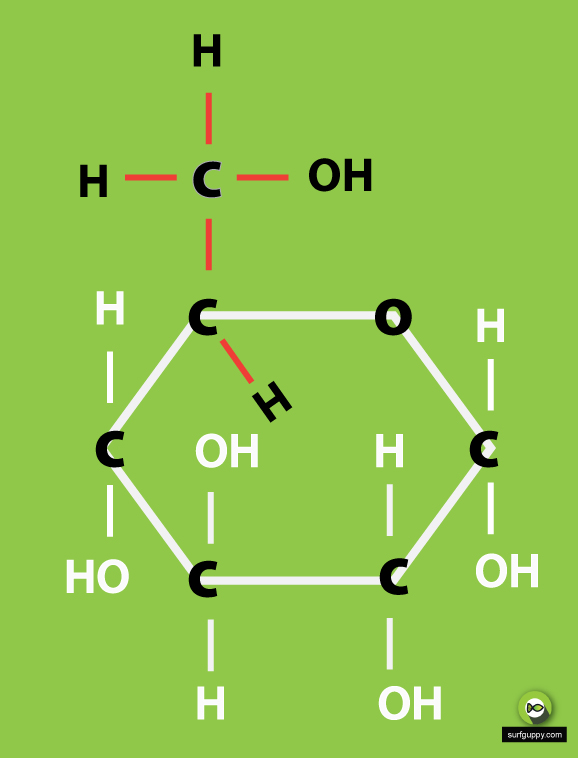



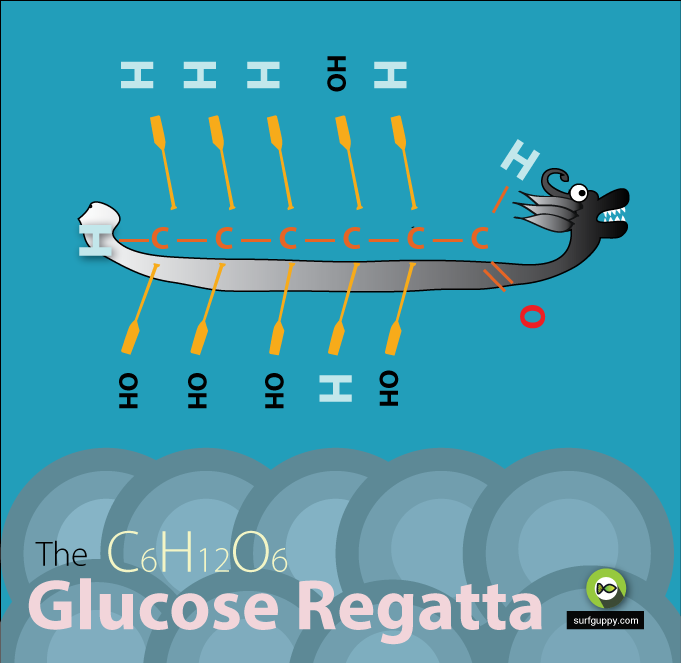
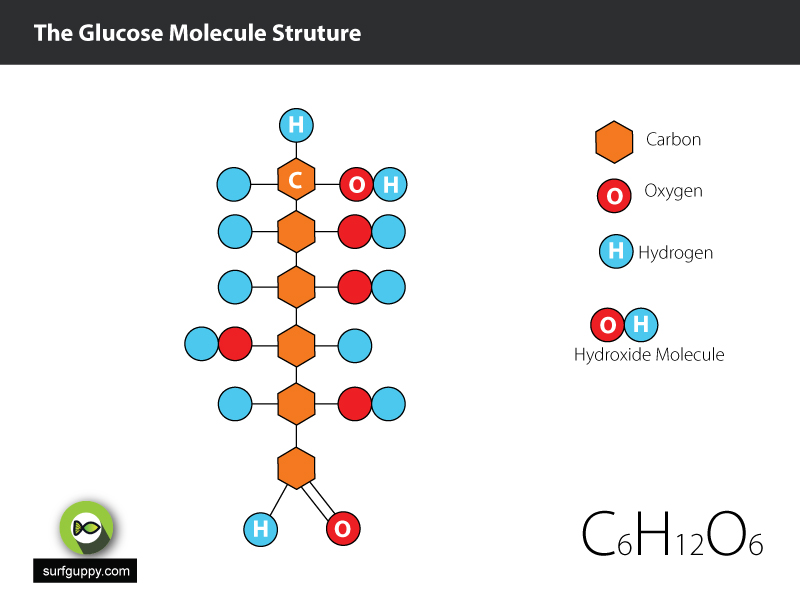
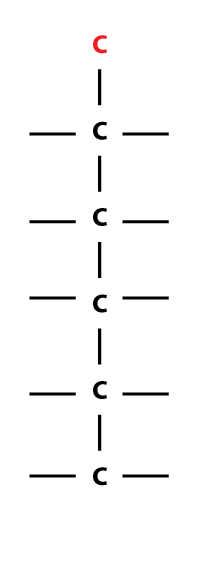
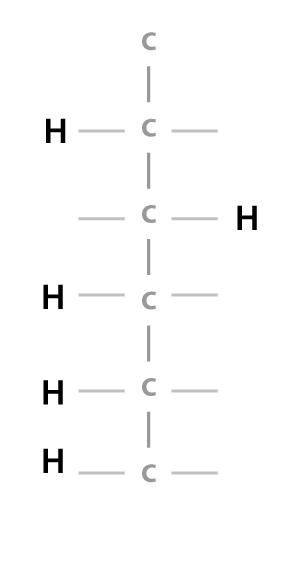


 …
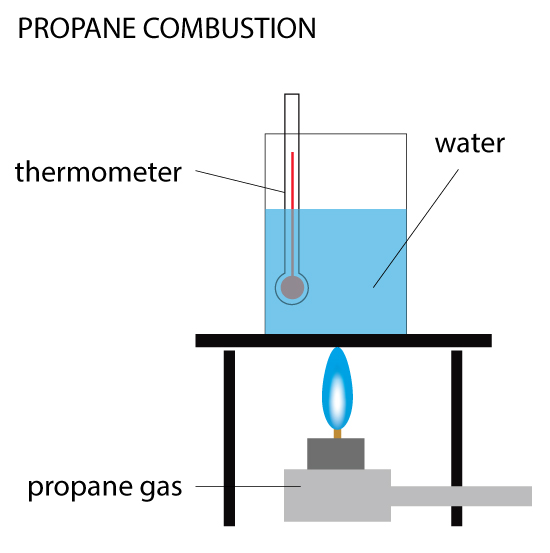
… 








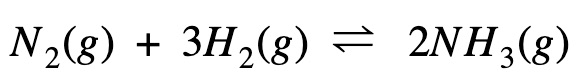


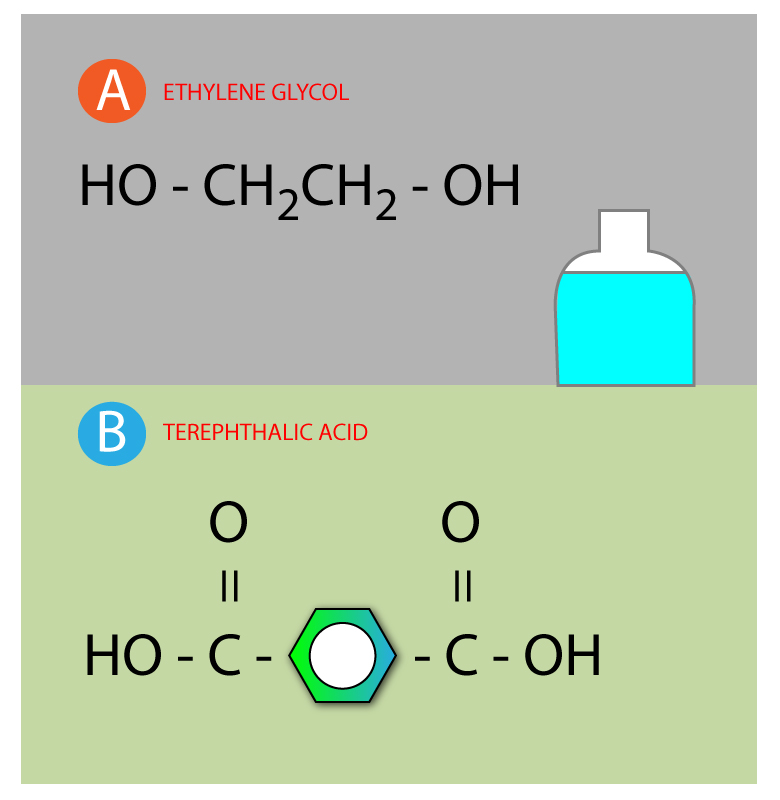
 This pretty symbol you see is called an ester linkage formed by combining acid and an alcohol.…
This pretty symbol you see is called an ester linkage formed by combining acid and an alcohol.… 
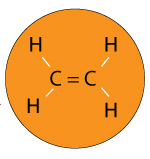 Imagine you have a polymer called Ethylene.
Imagine you have a polymer called Ethylene.