Why is water polar and why is the water molecule a bent shape?
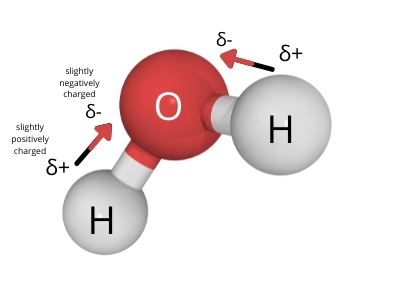
Water is polar because it has one end that is slightly negatively charged, and another end that is positively charged.
The water molecule is made of one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms.
The oxygen atom is covalently bonded to the hydrogen atoms. This means that the electrons between the oxygen atom and the hydrogen atoms are shared. Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share electrons.
However, the covalent bonds between the oxygen atom and hydrogen atoms are not shared equally. The electrons are pulled closer to the oxygen atom due to oxygen’s higher electronegativity.
Electronegativity is the measure of an atom’s ability to pull electrons closer to itself in a bond.
The unequal sharing of electrons in the covalent bonds make the bonds slightly negative towards the oxygen side and slightly positive towards the hydrogen side. The covalent bonds are said to be polar.
Since oxygen has only used up two of its electrons in the covalent bonds with hydrogen, it has 2 pairs of lone electrons – they are not used for bonding. The pair of electrons will repel each other as far as possible, so that the molecule will adopt a shape that is structually stable and has the lowest possible energy.
As a result, the water molecule assumes a bent shape. Due to the bent shape, the charges in the bonds do not cancel out. This in turn causes the whole water molecule to have charged ends. One side is slightly positively charged, and the other side is slightly negatively charged.
Due to its bent shape, the water molecule is polar. The unequal distribution of electrons around the structure of the water molecule causes the water molecule to be polar.


This website is a real game changer as a high school student. They explain it simple that I, myself, understood in less than 10 minutes.