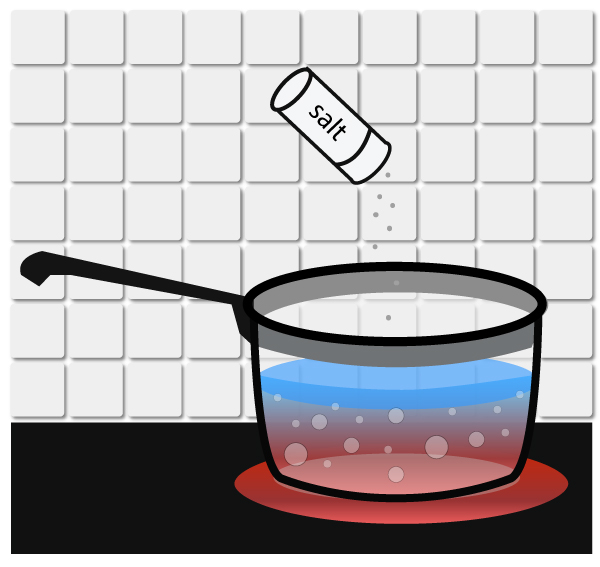
Boiling point elevation is the elevation of a solid’s normal boiling point by adding a substance to it.
When you add a solute (such as salt or sugar) to a pure solvent (such as water), the boiling point of the liquid solvent is now increased. This means that the solution will boil at a higher temperature.
Example, adding salt to water raises the boiling point of water from 100ºC to 100.04ºC.
The added solute decreases the number of water molecules at the surface. The solvent particles will now need more energy to push the solute particles out of the way and eventually escape into the atmosphere.
How atmospheric pressure affects boiling point
Further reading on how atmospheric pressure affects boiling point.
Adding salt to water
Do you ever wonder why some people add salt to water to cook pasta? Well, there’re a couple of good reasons for this. Not only does it make the pasta more flavorful, it also cooks it at a higher temperature. Putting salt to water increases the boiling point of water slightly so it will help to cook the pasta at a slightly higher temperature.
Adding salt to water will not help the pasta to cook faster since it will take longer for the water to boil. However, the raised temperature of the boiling point of water will help to improve the texture of the cooked pasta (makes it softer perhaps).
When salt is added to water, the salt particles hinder the water molecules from escaping from the liquid phase into the gas phase. This enables water to boil at a higher temperature.


