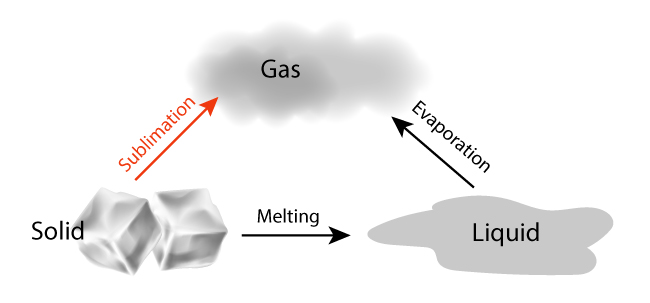
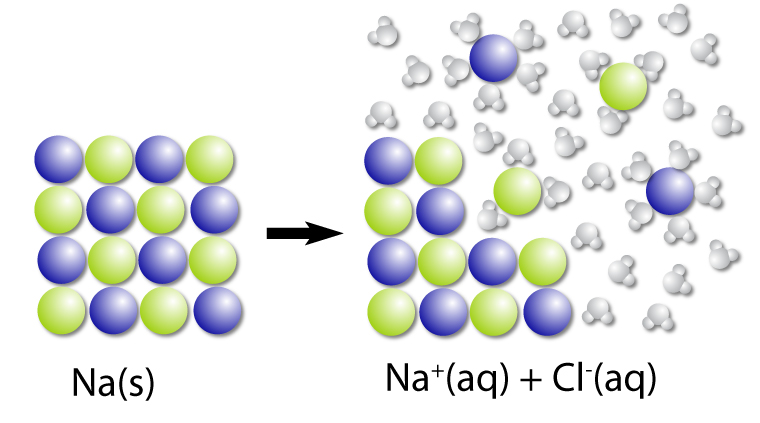
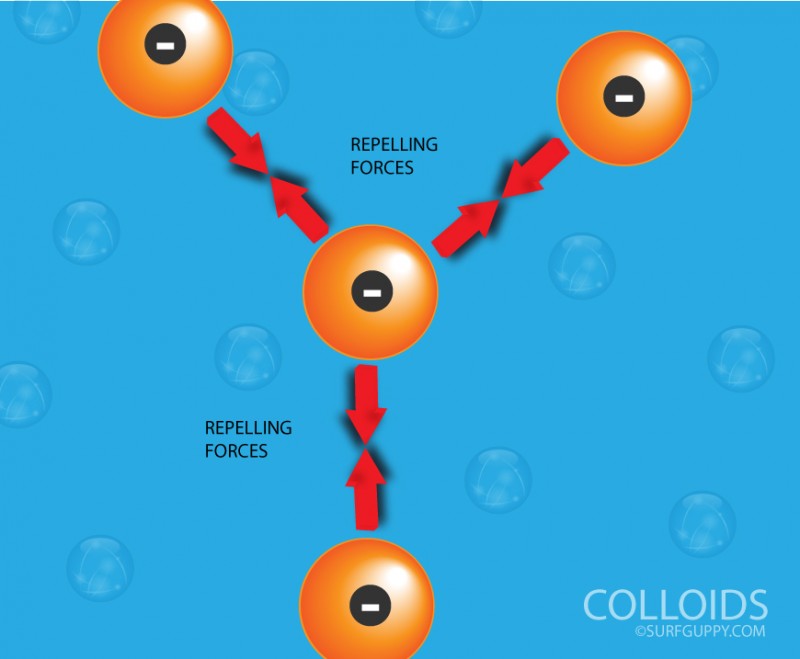
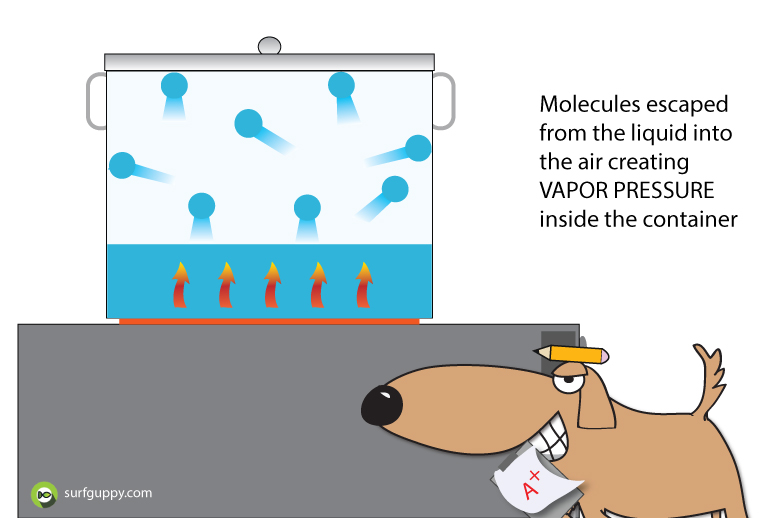
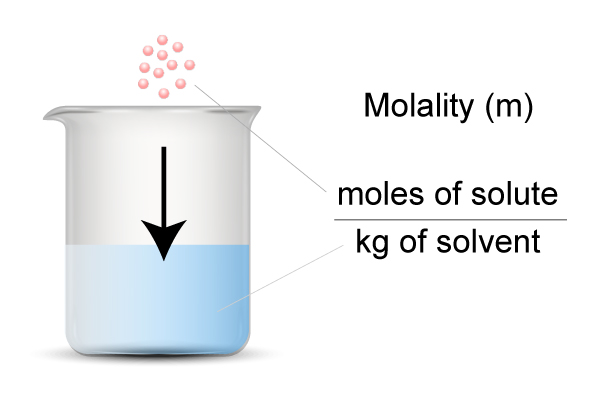
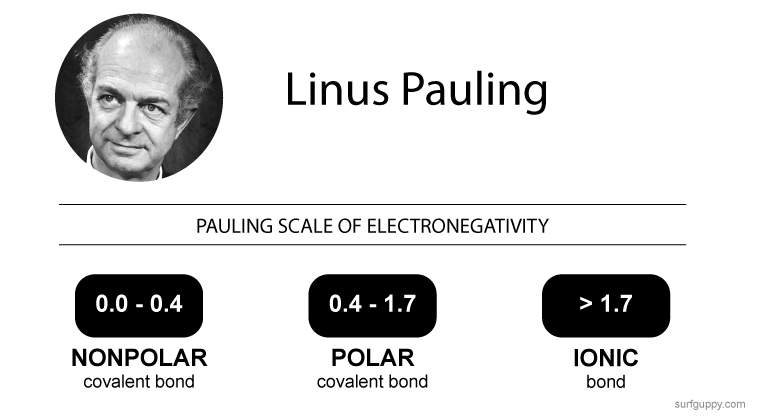
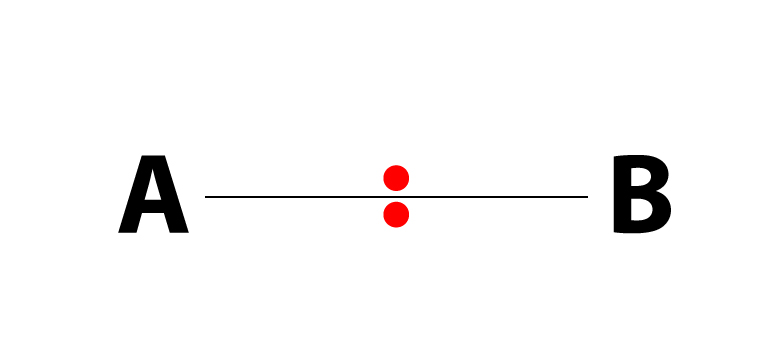
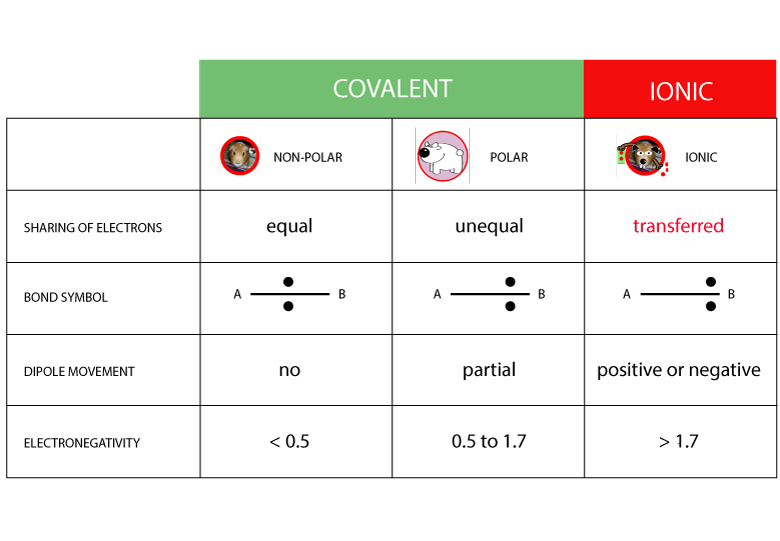
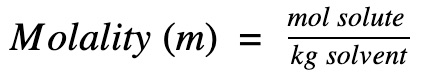What is Polymerization?
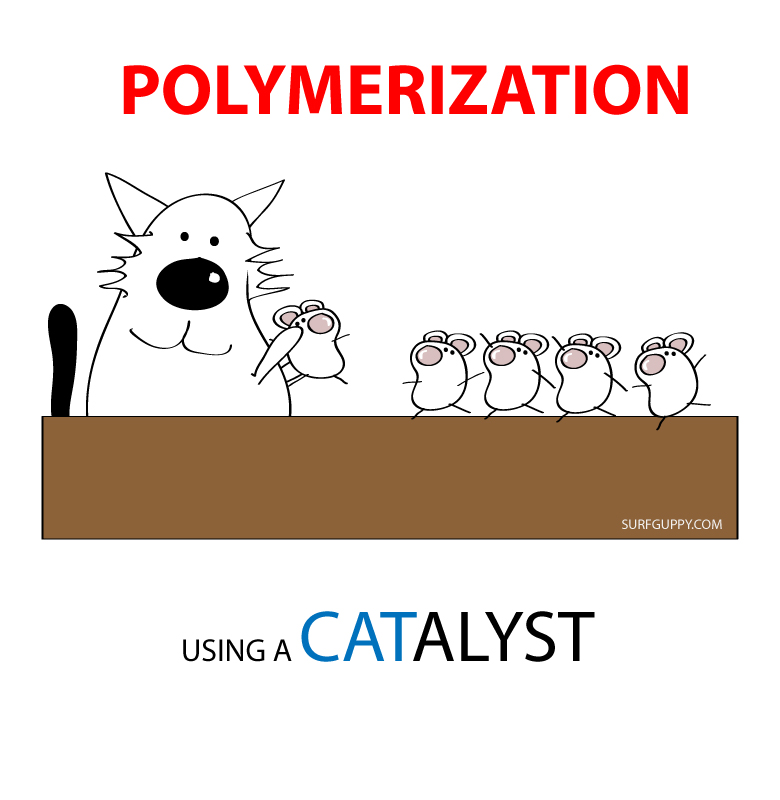
Polymerization is simply the process of putting together monomers (single molecules), to become a long chain of molecules (called polymers) with the use of a catalyst.
Polymerization is an important process for making plastics.
A catalyst

A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change.… Read the rest