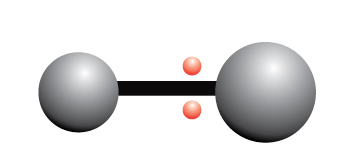
The electrons are unequally shared between two atoms
When a chemical bond involves “the sharing of a pair of electrons by two atoms in a molecule”, it is generally called a covalent bond.
In a polar covalent bond, the electrons are not equally shared between the atoms
Dipole moment
The unequal sharing of electrons causes a separation of partial charges within the bond. This separation of charges is called a dipole.
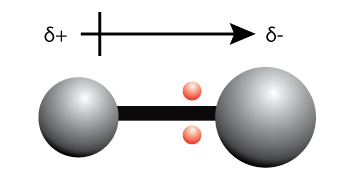
When the electrons are unequally shared between two atoms, one side of the bond becomes more negatively charged, and the other side of the bond becomes more positively charged.
We can use the term “partially positively charged” (denoted by the symbol +) and “partially negatively charged” (denoted by the symbol –) or to describe the effect of the unequal sharing of electrons.
A bond dipole is represented by an arrow as shown in the diagram above.
Electronegativity Bond Scale
Using the Pauling electronegativity bond scale, a polar covalent bond has an electronegativity difference between 0.4 to 1.7.
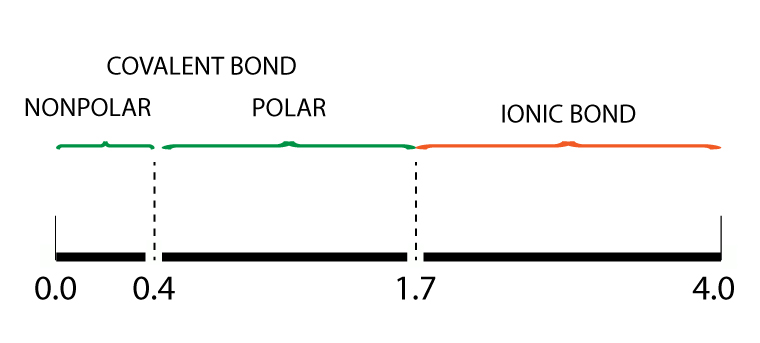
For more information on Electronegativity Bond Scale
Examples of polar covalent bonds
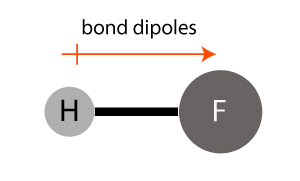
The hydrogen fluoride (HF) molecule has a polar bond between the atoms
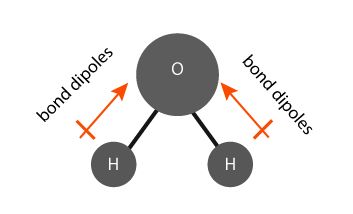
The water (H2O) molecule has polar bonds
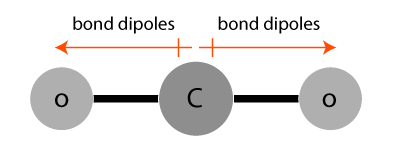
Bond dipoles in a carbon dioxide (CO2) molecule