
Hess’s law states that energy change in the overall chemical reaction is the sum of energy change or enthalpy change in the individual reactions that comprises it.

- Hess’s Law states that the heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical process is the same whether the process takes place in one or in several steps.
- Enthalpy change is the heat absorbed or given off during a chemical reaction.
- So, in other words, Hess’s law states that the enthalpy change in a chemical reaction is the same regardless of the path taken.
- For example, converting reactants A into products B, the enthalpy change is the same whether you take one step or several steps for the reaction.
Example
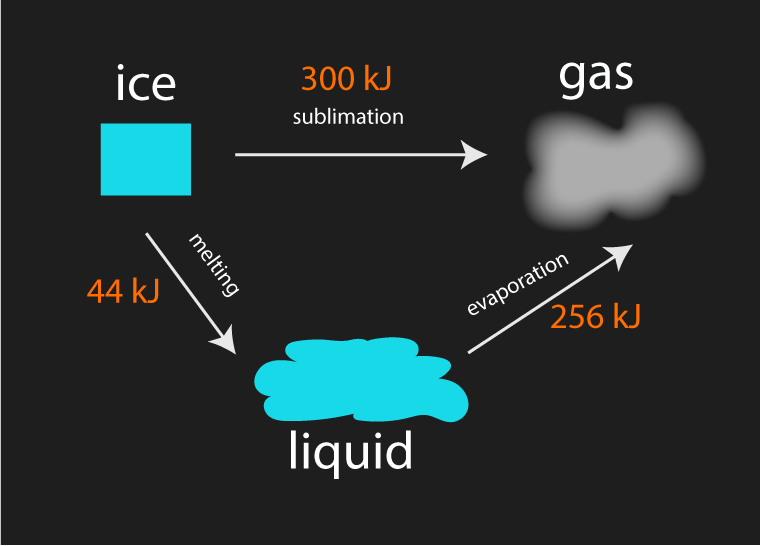
The above example illustrates that a block of ice takes the same amount of energy to turn to gas regardless of the path taken.
| Path 1 | sublimation | 300 kJ |
| Path 2 | melting + evaporation | 44 kJ + 256 kJ = 300 kJ |
Example of Hess’s Law Calculation – Methane Formation
Methane formation >>

