
In 1784, a French physicist and clergyman named Jean Antoine Nollet made an interesting discovery. He filled a pig’s bladder with a concentrated solution of alcohol. He then put the bladder in water and the bladder expanded!
This interesting process is caused by a phenomenon called osmosis.
Movement of water
Osmosis is the process in which water moves from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
The pores of the membrane are large enough for the solvent molecules to pass through but too small for the solute particles to squeeze through.
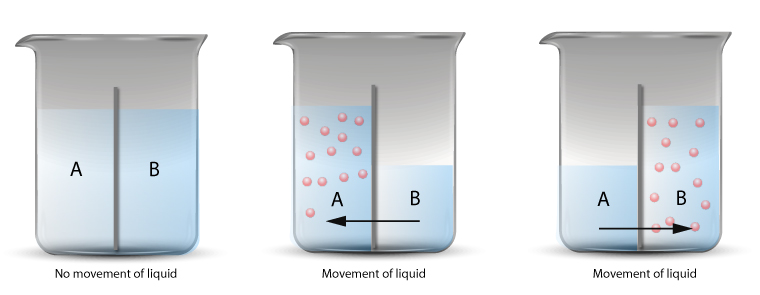
The diagram above shows the net movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane.
When different concentration of solutions are placed on either side of the semi-permeable membrane, there is a net flow of water molecules.
The osmosis process will continue until the system has reached equilibrium state.
The equilibrium state is the state when both sides of the membrane has reached the same concentration.
Osmosis in Plants
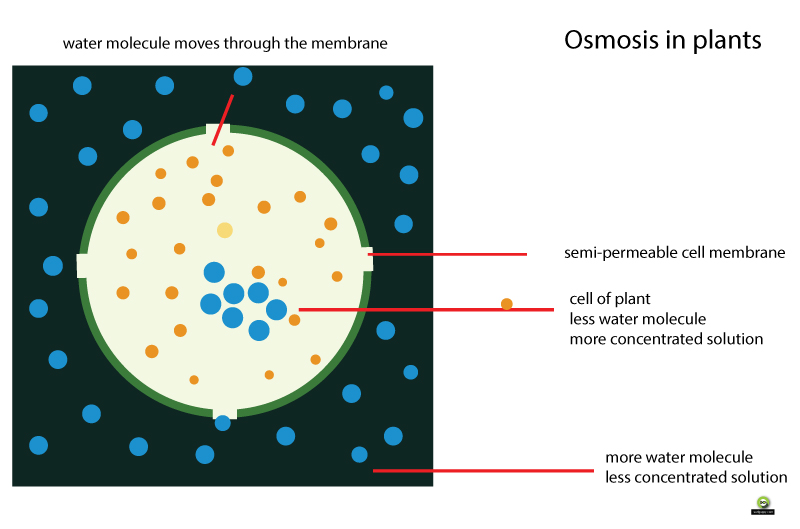
Use the diagram above to help you visualize osmosis in a plant cell.
When you water a plant, the plant absorbs the water using the process of osmosis.
Water moves into the plant cell because there are more water molecules on the outside of the cell than inside.
If you take away the semi-permeable membrane, osmosis will not occur, only diffusion. The fact that water is diffusing through the semi-permeable membrane is called osmosis.
If you water the plant with a concentrated salt solution, the plant will wither away because water will be drawn out of the plant.

