
In addition polymerization, all the original atoms present used for making the polymers are retained in the end product.
How to convert monomers to polymers?
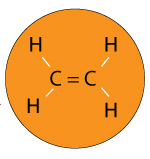 Imagine you have a polymer called Ethylene.
Imagine you have a polymer called Ethylene.
Ethylene is a single molecule with the formula CH2H4.
It’s double bonded so the molecule can be represented as H2C=CH2
A double bond is a bond between two atoms sharing two pair of electrons.
Read more on single, double & triple Bonds
Convert double bonds to single bond
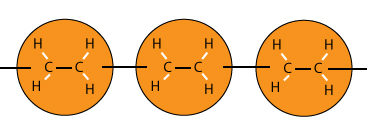
To form a polymer of molecules, the double carbon to carbon bonds are broken to become single bonds.
Another important aspect is the open bonds at both ends of the polymer to allow for more linking of molecules.
To change from a double bond to a single bond, replace the C = C to C – C. And don’t forget the catalyst which contributes to the process but does not need to be shown in the equation.
And don’t forget the catalyst which contributes to the process but does not need to be shown in the equation.
The catalyst helps to speed up the reaction but itself does not undergo any chemical change.
Vinyl chloride becomes polyvinyl chloride
Start with the structural drawing of the monomer
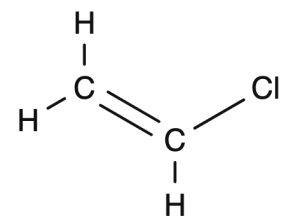
Make three repeating units of the monomer
Propene becomes polypropene
Start with the structural drawing of the monomer
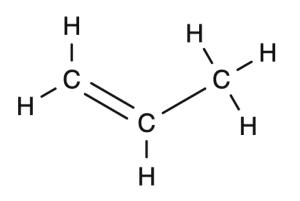
Make three repeating units of the monomer
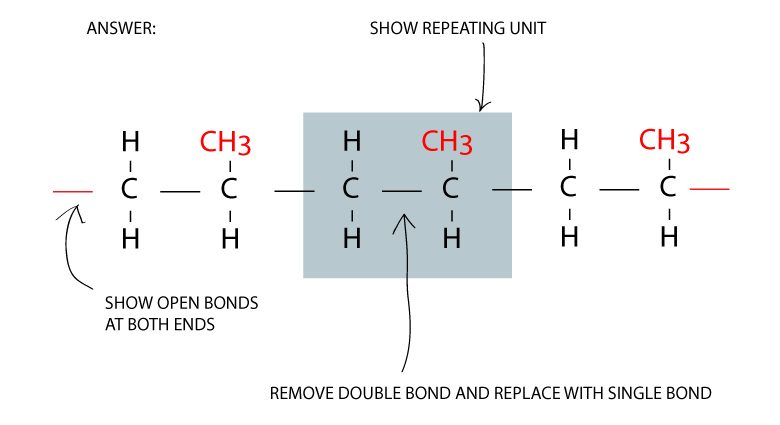
Convert double bonds to single bonds
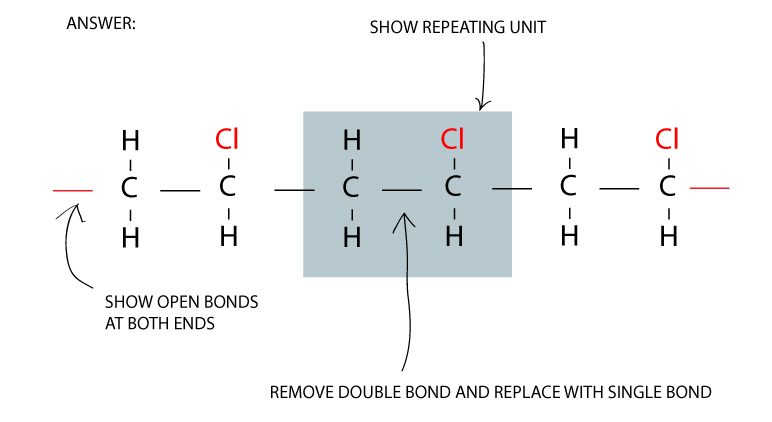
You can construct a polymer structure from a monomer from the following steps:
- Show the repeating unit for the nth term
- Replace double bonds with single bonds
- Place open bonds at both ends

