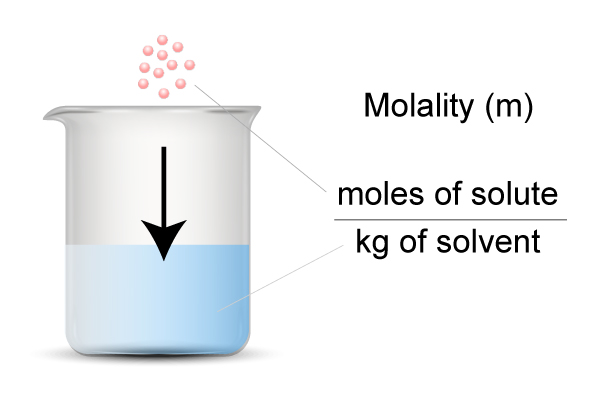
Molality is defined as the number of moles of solute per 1 (kg) of solvent.
- Solute = particles you dissolve
- Solvent = the liquid you use for dissolving the particles
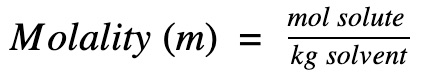
Example
Calculate molality (m) of 29.8 g of glucose (C6H12O6) dissolved in 622.8 g of water
| Symbol | Element | Atomic weight | Atoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | Carbon | 12.01 | 6 |
| H | Hydrogen | 1.008 | 12 |
| O | Oxygen | 16.00 | 6 |
Step 1. Find the molar mass of glucose
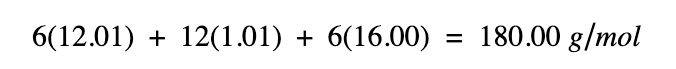 |
Step 2. Find the number of moles of glucose
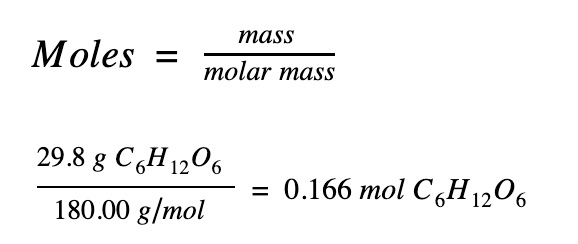 |
Step 3. Find the concentration of the solution
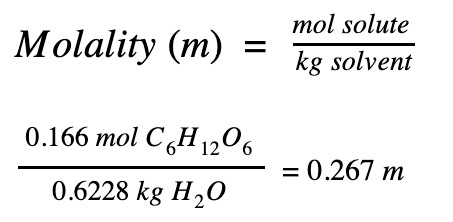 |
29.8 g of glucose (C6H12O6) dissolved in 622.8 g of water
The concentration of the sugar solution is 0.267 m.

